Each time you do a search in Google, what do you see?
Yes, there's a page of search results...
But what else do you notice?
Well, there's paid ads on the right and top. Below them are the organic results.
If you're like most searchers, you may well prefer clicking on the organic search results, as opposed to the paid ads.
In fact, numerous studies have shown if you want to really benefit from this traffic and its clicks, your website should be placed at the top of the first page of organic search results.
The numbers don't lie either. The first five organic results on page one account for over 75% of all clicks. So if you really want high volumes of quality traffic, paying for Google Ads is simply not enough.
But here's the thing.
Google's colossal processing power not only handles over 3.5 billion search queries every single day.
It sorts all those search results too.

But how can your website get a top ranking spot on page one of google?
And generate more visitors than you ever thought possible?
Well, to get better organic rankings, you'll need to communicate with the search engines. To do that, you'll need to learn the language of SEO.
And, you can make a great start by taking advantage of your HTML tags.
What are META Tags?

A META tag is simply any tag that appears within the header tags (<head>...</head>) of your website.
Effectively, it’s a way to provide search engines with useful information about your site.
In this case, 'META' means information about information. For instance, the TITLE tag is a META tag which tells Google (and also the human visitor) what your web page is all about.
Looking under the Hood of your Website

Know your HTML Source Code
HTML is simply the 'mark up' code used to create a web page. Web browsers use this code to figure out how they'll display a page's content.
To view the source code of any page (and the meta tags it contains), just use the following commands:
- On a PC: CTRL + U
- On a Mac/Chrome: View > Developer > View > Source
Anatomy of the Search Results
Your Website is a Billboard

Picture thousands of cars driving down a road. On the roadside are rows of billboards, but only one advertises your website. This is you site in the search engine results. To attract attention from the car drivers, you'll need to entice them with your advert.
What a Typical SERP Looks Like
Let's take a peek at what the SERP (Search Engine Results Pages) looks like for a search like "digital marketing strategy"
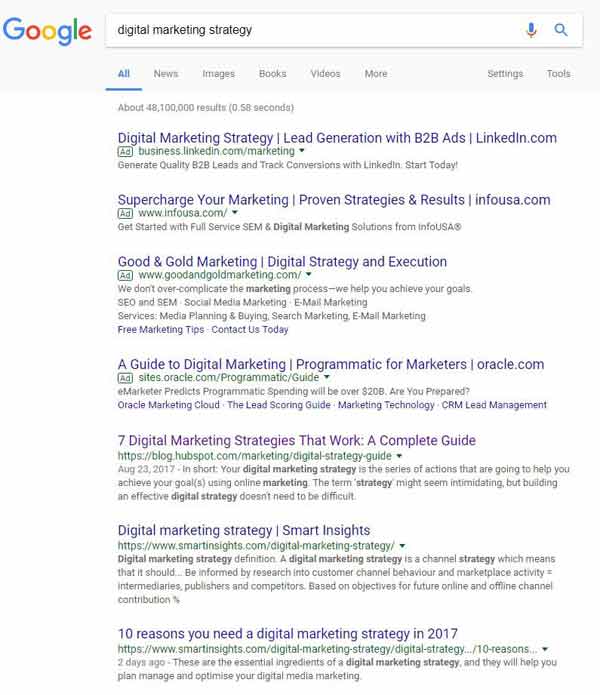
What do you notice?
Yes, you can see the title, description and URL (snippet) of each site in the results.
Google pulls that information from the title (the blue link) and description (text below) meta tags in your website's HTML code.
Taking a Closer Look at the HTML Source Code
Let’s go back to our search results for the term “digital marketing strategy”, and take a closer look at the #1 ranking site.
Here's a screenshot of the source code for HubSpot's 7 Digital Marketing Strategies Guide page:
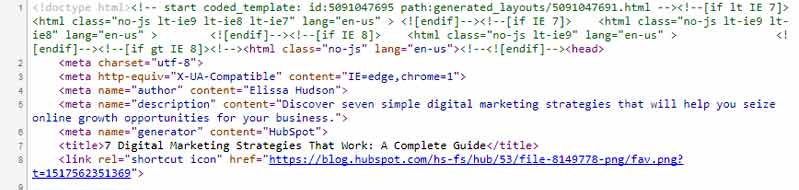
The source code of any page on the web, will look something like this. Search engines like Google read your source code to find out exactly what your website is about.
Here's a HubSpot's snippet of the top organic search result:

So looking at our HubSpot page's source code:
- the TITLE tag is saying to Google, "Hey, this is a page all about: '7 Digital Marketing Strategies That Work: A Complete Guide’”, and;
- the META description is saying, "Hey, Google, if you like this summary, you can use it in the search results: 'Discover seven simple digital marketing strategies that will help you seize online growth opportunities for your business.', or you can use content from the page instead", and;
- there are no META keywords tags, which is all good, because Google ignores it.
Why META Tags Matter
Get Your Website Seen
You may think that your website is a mere speck in the millions of search results that google spurts out.
But, the search engine results have 3 elements you certainly DO have control over:
- your website's title
- your website's display URL
- your website's meta description
A well-crafted snippet can not only drive clicks and users to your site, but move you up the rankings.
Remember, you have less than 2 seconds before a user decides whether to click on your advert, or not.
META Tags and SEO
You may have heard that META tags don't matter or they are all that matters.
META tags ARE an important part of your SEO strategy. They're not the only piece. But, they do lay a solid foundation for any future SEO work.
HTML elements like META tags are important as search engines can pick up certain ranking signals from them. Some of the most important elements to achieve SEO success are right below.
Optimising Your Meta Tags
1. Title Tag
If you're serious about SEO, having a well optimised title is a crucial element for any web page. In the header of your web page's source code, you can find it bounded by title tags, like this:
<title>...</title>
And here's a real example of the tag from the HubSpot html code:
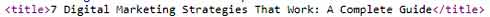
They are actually the title that is displayed in the user's browser, when they visit your page.
Titles are still the most important HTML signal you can use to increase your rankings. Search engines like Google use title tags to understand what a page is about. Titles are key to how search engines weigh your page's relevance, and can have a big impact on a searcher's propensity to click through.
A title tag should be used to describe the main topic of your web page. Identify the keyword your page is targeting, using your previous keyword research.
Craft a unique, descriptive title for your page. The main keyword should be placed towards the beginning of the tag, ideally under 65 characters. Give it some 'Ooommph' to make people want to click it.
In the above HubSpot title tag, for example, "digital marketing strategy" is close to the start of the title tag. Titles should be unique for every page.
2. Meta Description Tag
This is the second most important tag, and appears in the search results as the second piece of text right underneath your title tag and website URL. It's wrapped in the meta name="description" tag like this:
<meta name="description" content="....">
And here's the tag in HubSpot's html code:
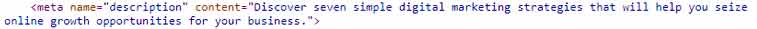
Purists may argue the meta description tag doesn't help your pages rank higher. It's true that this tag is more of a display element. But, it's still helps how you appear in the top search results and could still be classed as a success factor.
Say a user searches for "digital marketing", and your description contains these keywords, then these will appear bolded in your snippet so have more chance of catching the user's attention. Additionally, a good meta description can help sell your prospective website visitor the end result will be relevant to what they're looking for. Both are directly related to increasing your click-through rate.
Some websites tend to skip over this step. This means they will have the same meta description on each page. This may result in duplicate meta description issues (usually reported in Google Webmaster tools). This in itself, may not be a huge problem, but they're ruining their chances of taking advantage of free advertising. The meta description is an extra couple of sentences further describing what your page's primary content is about.
There’s another downside of not writing your own high-quality description. Google will often supplement content on the page with your meta description, if it either does not find the description tag or finds the keyword on the page and wants to display it to the user.
It's crucial for the same main keywords used in your title tag to also appear in the meta description. There needs to be continuity between your title tag and meta description. This is so search engines can understand what your page will be talking about.
For example, say your main keyword phrase is "digital marketing", and you use it in your title tag. But, your meta description has the phrase "SEO techniques". The search engines won't be able to determine what the page's core content is about. This inconsistency between the tags will confuse search engines, so they may well rank you lower.
Write a strong, concise sentence or two (between 120-150 characters). Make sure it contains your main keyword, and is relevant to both your headline and the article's content. It should not only describe the page, but like the title tag above, be click worthy.
Here's what Matt Cutts has to say about tweaking your titles and descriptions to improve your CTR:
3. Header Tags
Header tags go right into the content itself and are primary navigation elements. Headings are used to logically lay out your web page, as well as help a reader's navigation of content. They define the main sections of self-contained content on your web page. There are actually 6 different heading tags. In your HTML code, you may have h1, h2, h3, h4, h5 and even h6 tags. A header element is primarily used to organize your page into readable blocks of content with topical headings and sub-headings (child elements). Heading tags are usually formatted from large (most important) to smallest (least important).
Header tags are wrapped in html tags like this:
<h1>...</h1>
<h2>...</h2>
<h3>...</h3>
h1 tags may seem less important than they used to be, but still worth doing. The h1 heading is a page's main heading.
Your aim for h1's is to write copy that will be warm and inviting enough to get people to read the rest of your content. Make them think "Yes, that's really interesting; I wonder what's on the rest of the page?"
It's Ok to use something similar to the title tag's content in the H1. It should contain the main keyword (or a long tail variation ofit), but don't keyword stuff. That is, include your primary keyword at least once in the heading tag (but it doesn't need to be an exact match). Like all aspects of SEO, don't overdo it!
Make it feel naturally appealing and engaging. Keep it between 20-70 characters. Your aim is to compel your visitor to read more of your content.
Here's the source code view of a h1 tag:
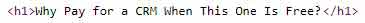
And here's what the source code view of h2 and h3 tags looks like:
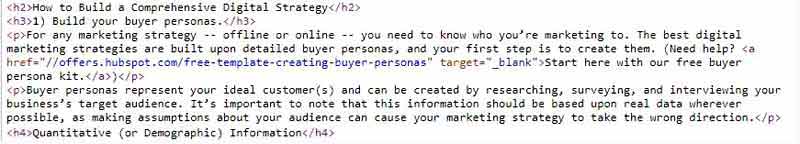
No Nonsense Heading Guidelines:
- The h1 tag serves as the title for the whole page. Don't use it as for subheadings. Ideally, only use one for each page. Using more than one h1 can confuse the search engines about the topic of your page.
- Use subheadings consistently to make the content palpable. Don't mess with the order that heading tags are intended to be used. Create a clear top-down heading hierarchy so search engines can understand them. For example, don't skip to h3 tags without using h2 tags first; or use h3 tags when they would better be h4 subsections underneath another h3 tag, etc.
- For short posts (under 1000 words), you may only need to use h1 to h3 tags to structure your piece of content. An example heading tag structure would be to use the h1 tag first, then the h2 tag followed by 2-3 h3 tags underneath, then another h2 tag followed by 3-4 h3 tags underneath, etc.; in this scenario, there's no need to use the h4 to h6 tags. In fact, the use of h5 and h6 tags is rare.
- Spread your secondary and long-tail keywords throughout the h2 - h6 sub-headings without keyword stuffing.
- Avoid using formatting instead of subheadings. For example, using size, colour, bold formatting in place of h2 or h3 subheadings. As mentioned, subheadings are recommended as they give search engines a clear structure, so they can interpret what your page's central content is about.
- Avoid using heading tags in the menu or navigation. For example if a common header for different sections of your site have the same h1 tag. This can lead to keyword cannibalization and confusion of which content belongs to the body.
4. Image Alt Tag
Optimising Alt (alternative text) tags is another easy SEO win that many web masters miss out on (especially if you're in e-commerce).
Here's what the alt tag looks like:
<img src="https://your-website.com/assets/logo" alt="your site logo">
Here's what the alt tag looks like in the page's source code

It can be all too easy to ignore all the photos and screenshots on your web page. But here are two facts:
- people search in Google under the 'Images' tab (not just the 'All' tab), and;
- search engines can read words, but can't read images
This means to rank your page's images on Google, you'll need to include alt tags for your pics. The image alt tag tells a search engine what your image is about, helping your image become higher in the image search. And also helps accessibility of your site (for someone who may not be able to see your site).
Avoid using Alt tags for website design images like CSS styling or borders. Do use Alt tags where appropriate, for example: logos, screen shots, team member profiles, product pictures. Have a unique alt tag text for each image.
Think about the users of your site. Visually impaired surfers rely on ALT tags when visiting websites. Special browsers or screen readers help them to read the alt tag's text of images on a page.
Think more about how you would describe the image to visually impaired person. Describe the image as a human would see it. Use natural, user-friendly language. Simply use a clear, concise description of up to 6-7 words, which is not stuffed with keywords. e.g. for a page about ford trucks, use a descriptive tag:"blue ford truck" NOT "home page graphic 1" or "buy ford trucks" (if your main keyword was "buy ford trucks").
From a ranking perspective, search engines look not only at the alt attribute, but the image's title, file name and surrounding text. When an image is linked to, it's alt attribute acts in a similar way to anchor text in a text link.
Get this right and people will easily find your visual content.
Here are some tips from Matt Cutts:
5. Links and Anchor Text Tags
What does a Link look like?
This is what the HTML tag for a link (and anchor text) on any web page looks like:
<a href="https://www.your-website.com">anchor text in link to your website</a>
Here is a link in the source code:

In the above picture, the actual link is coloured blue and the anchor text is "web analytics"
Why Anchor Text Matters
The text you use in your links matters!
Sprinkled throughout your content, you’re likely to link out to different sources.
You may want to give a reference to relevant sites that have useful data or images. This also makes sure you give credit to the original source.
Many people just link to a site without even giving a second thought to the anchor text in the link tag. But, they're missing out on boosting their chances of SEO success.
But, search engines factor in HOW you link to your other content as a clue to what that content is about.
The text "anchor text in link to your website" represents what's known as anchor text.
Google looks at anchor text to understand exactly what a link is about. It's trying to find out whether you are linking out to a relevant page and what the topic is?
Good anchor text will answer these these questions.
So if you link out to a relevant page on your own domain, you are keeping your content organised, which in turn, helps your domain's authority. Google love relevant content that's organised.
Linking to someone else's web page with a good, anchor text, will help their rankings too.
Anchor Text Guidelines:
- Do write natural text
- Use short, descriptive text (several words or a short phrase)
- Avoid using lengthy anchor text
- Avoid generic text like "website" or "click here"
- Avoid over optimising, by keyword-stuffing
- Do format links so users can easy to spot them
General Link Guidelines:
- Click depth is important;
- the closer to the root domain, the better
- The location of the link is a strength factor;
- in-content links are more valuable than footer/sidebar (blog-roll) navigation links
6. No Follow Link Tags
Follow or No follow Links?
Follow 'links' are inbound links to a page that count as a vote for that specific page. The more relevant, authority backlinks a page has, the more it will help push a page higher in the SERPs.
Conversely, a no follow link leads a sad and lonely life. It's a link on a web page that doesn't count in the page's favour, and doesn't help a page's search rankings.
The 'nofollow' attribute signals to Google: "do not to follow the link to the next page"; that is, you don't want the search engines to focus on the next page. This means Google will not transfer PageRank or any other ranking signal across a 'nofollow' link. Instead, you can direct the search engines towards things you think are more important.
How to Create No Follow Links
No follow links look like this:
<a href="http://www.yourwebsite.com/" rel="nofollow">Link Anchor Text</a>
A no follow link is created with the 'nofollow' attribute.
The nofollow attribute (or tag), is effectively a sign for the search engines which says: "don’t count this backlink". You can add rel="nofollow" to any links you don't want search engine crawlers to follow.
When to Use No Follow Tags
You might be wondering when to use the no follow tag. No follow links should be mainly used for: paid links (e.g. sponsored content or native advertising), blog comments (to keep comment spam down), forums, 'untrusted content' (as defined by google).
Previously, webmasters used the "nofollow" tag to page sculpt. They were directing 'link juice' to specific parts of their site they wanted visitors to focus on. It's recommended not to do this practice and, instead just use it for editorial purposes and in your blog comments.
In general, nofollow links can't hurt your site's ranking:
Ultimately your website should always maintain a healthy balance of do follow and no follow backlinks. Both deserve a place in your perfect link profile.
7. Canonical Tag
The canonical tag is great for helping search engines prioritise one web page over a duplicate one.
This is what the canonical HTML tag looks like:
<link rel="canonical" href="http://www.your-website.com/" />
Say there are two identical pages that exist on the web (e.g. if you've syndicated another site's article) the Canonical Tag should be included, containing the originally published page's URL.
You may be thinking your site doesn't have any duplicate pages.
Well, every site may have duplicate web pages.
Let's take a look at just one example.
A search engine may crawl ONE web page but use all these different URLs:
http://your-website.comhttps://your-website.comhttp://www.your-website.comhttps://www.your-website.com
To us, they may appear to be the same page. However, for a search engine, each variation is viewed as being a duplicate.
Some sites have thousands of duplicate pages. This becomes a problem when search engines try to rank your content. By confusing the search engines, it will choose just one URL and rank it much better than the rest.
You can easily fix this problem, by using the canonical tag. This specifies which URL you want the search engines to pay most attention to.
Use these guidelines to help Google read your website and rank you higher.
Top Tips
1. For Title and Description tags
- Look at Adwords ads for your key search terms. If advertisers are spending money, it means they must be working. Obviously don't copy the ads word for word. Use them for some meta tag inspiration!
- An easy way to create and optimize tags for Wordpress blogs is to use the Yoast SEO plugin.
2. Use Google Search Console
- If your site already has traffic, e.g. more than 6 months old, you can optimize the tags. In Google Search Console, see which keywords are driving traffic to specific pages.
- Consider including those keyword phrases into the title tag and meta description for a page. You will see your ranking increase over time.
Final Thoughts
HTML tags are a free and simple way to boost your website's SEO.
If you have you never tried optimising your tags..
Check it out today!
